As we all know, Google Analytics is a tool developed by Google. Anyone who has worked or is currently working in SEO is very familiar with it. Google Analytics is an analytical tool that tracks your website visitors or traffic once you install its code on your website.
This tool is very popular in the SEO industry. It provides detailed reporting on your visitors—from the number of users to their behavior, including how they arrived, from where, when, and why. Google Analytics has always been the first choice for professionals in the SEO field. Over time, it has evolved from Universal Analytics to GA4.
Despite its vast popularity and status as one of the most authoritative tools, many SEO professionals have observed that Google Analytics doesn’t always update or report traffic accurately. Sometimes, there are discrepancies in the data, even when content is ranking well.
This article will focus on Google Analytics tracking issues—when and how it tracks data, and when and why it fails to track users properly.
The real challenge isn’t that Google Analytics doesn’t track data—it’s that most people don’t know when and how it fails to track users and traffic, especially when the following issues occur.
Let’s explore some of the most common reasons why Google Analytics may not track users accurately.
1. Incorrect Tracking Code
The most common cause is a poorly implemented or missing tracking code. Ensure the Google Tag is correctly placed on all relevant pages. Sometimes, the Google Analytics code is placed in the wrong location on the website, which prevents Google from tracking data accurately.
There is a specific place to add the tracking code on a website—place it in the head section, just above the body tag. Placing the tag randomly within other scripts can cause tracking issues or prevent Google Analytics from collecting data altogether.
If you’ve added your GA code in the correct place, the next step is to check whether your Google Analytics property ID and script are correct. You can verify this by going to your Google Analytics account, selecting the appropriate property, and checking the data stream settings.
Note: If you haven’t installed the GA tracking code manually, you can do it using a third-party tool, website builder, or CMS. In such cases, you’ll need to add the property tracking ID.
2. Linking Issues with Google Ads:
Suppose you are running Google Ads and visitors are coming to your website through those ads, but your Google Ads account is not connected to Google Analytics, or auto-tagging is not enabled. In that case, you might see discrepancies in the reports or see “not set” in Google Analytics.
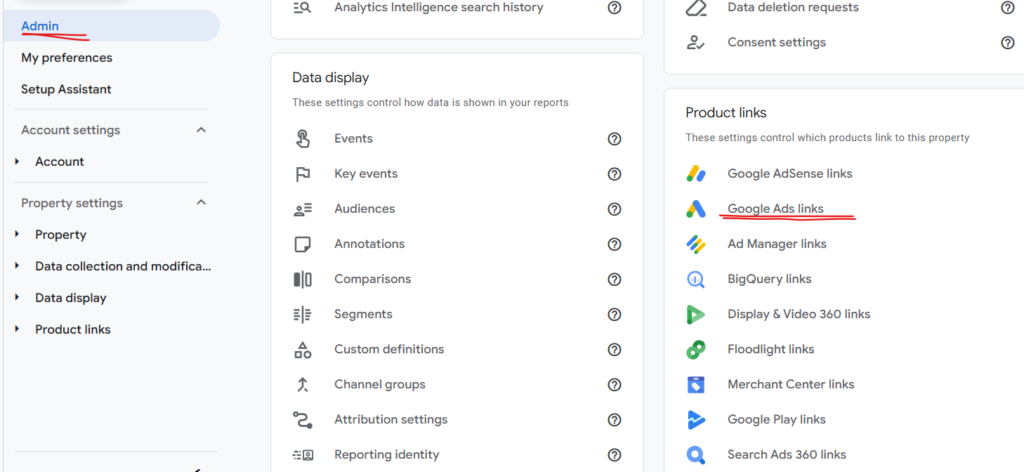
To connect your Google Ads account with your Analytics property, go to Google Analytics, open your property, click on Admin, and then find the Google Ads Linking section on the right side of the page.
3. Browser Privacy Settings and Extension
Sometimes, browser extensions can block GA4 from collecting data. Some browsers also have privacy settings designed to protect user data, which can prevent Google Analytics from tracking and collecting information.
Below are the Privacy-Focused browsers that;s block the google analytics to track the data of your visitors:
| Browsers | Default Tracking Protection |
| Brave | Blocks Google Analytics by default |
| Firefox | Enhanced Tracking Protection may block GA |
| Tor Browser | Strongly restricts all tracking scripts |
| Safari | Limits tracking with Intelligent Tracking Prevention (ITP) |
4. Ad Blockers:
We install ad blockers to stop ads or prevent random scripts from tracking data. These ad blockers can also prevent Google Analytics from tracking data. Below are the most common examples of ad blockers and extensions.
| Extension Name | Browser Compatibility | What it does |
| uBlock Origin | Chrome, Firefox, Edge, Brave | Blocks requests to www.google-analytics.com and other trackers |
| Ad block plus | Chrome, Firebox and Edge | Commonly blocks GA4 and other tracking scripts |
| Ghostery | Chrome, Firefox and Edge | Blocks analytics, ads, and social tracking scripts |
| Privacy Badger | Chrome and Firefox | Automatically blocks GA and third-party trackers |
| No Script | Firefox | Prevents all JavaScript, including GA tracking code |
| Duck Duck Go | Chrome, Firefox | Blocks Google Analytics as part of its tracker protection |
Tips you can consider:
- Consider server-side tracking
- Use additional analytics tools like Plausible or Matomo
- Monitor trends via Search Console, not just GA4
5. Consent Issues:
Websites add cookie consent options, asking users to accept or reject cookies. Some websites even require users to accept certain types of cookies to continue browsing.
If visitors reject the cookies, Google Analytics cannot track their data. For GA to track users, they must accept the cookies.
Sometimes we see that content is ranking or we’re getting more traffic, but Google Analytics doesn’t show as much data as expected. Our observation may be correct, but if visitors reject cookies, GA is unable to track them.
6. Data Processing Delays
Google Analytics does not update data instantly on the dashboard or in the reports section. Sometimes, it can take 24–48 hours for the data to be fully updated in the system. If you’re checking data from yesterday, it’s possible that it hasn’t been updated correctly yet. Before reaching any conclusions, it’s best to wait for the data to be fully updated in GA4.
7. Filters:
Google Analytics provides many filter options for reporting. Filters allow you to include or exclude specific data in your reports based on what you want to analyze or keep.
If you configure filters to exclude data from certain websites, sources, and so on, you may notice differences in the data shown in Google Analytics. This can result in a discrepancy between actual website visitors and what is reported.
Below are the some common filters in google analytics:
- Internal Traffic Filter: Exclude traffic from internal teams or company IP addresses to avoid skewed data.
- Developer Traffic Filter: Filter out traffic from developers using debug_mode or debug_event parameters during testing.
- Event Name Filter: Include or exclude specific events (e.g., page_view, purchase) in your reports.
- Geographic Location Filter: Filter traffic based on country, region, or city for localized analysis.
- Device Category Filter: Segment traffic by device type, such as mobile, desktop, or tablet.
8. Duplicate Tags or Conflicts
The tracking code should be implemented only once on the website. If multiple GA tracking codes are implemented, it can cause issues with website visitor data. There could be two possible situations: the codes may conflict with each other, or a single visitor may be counted multiple times.
It is very important to check your Google Analytics tracking code—whether it is implemented properly on your website. Check if it appears multiple times; if so, keep only one. Ensure it is placed in the head section, above the body tag. You can also add the tracking code server-side to avoid these issue
If GTM Tags or manual tag firing together it may cause double counting or missing hits because of conflicts.
9. Debug Mode Enabled
Make sure you are not in the DebugView of GA4. You must check the main reports to see the actual data collected by Google. If you are in DebugView, it may appear as if no data is being collected.
- If you’re using DebugView in GA4 and not checking the main reports, it may seem like no data is being collected
Fix: Make sure you’re reviewing the actual live reports, not just debug sessions.
Below are the Tools to Troubleshoot GA4 Tracking
- Google Tag Assistant Extension
- GTM Preview Mode
- GA4 DebugView
- Real-Time Reports
- Network tab in Chrome DevTools
Conclusion
In this article, we discussed the possible reasons why Google Analytics may not be tracking your visitors. Many people face the issue of Google Analytics not showing real or accurate data—we expect more traffic but don’t see it reflected in the reports. As covered, these are some of the most common reasons why Google Analytics may fail to track your visitors.
Happy reading!